
Server will then acknowledge the IP address leasing with unicast ACK message and that’s it. After the HDCP replies with unicast DHCP offer host will one again use broadcast to send DHCP request to server. Host that connects on the network will in the first step send broadcast DHCP discover message in order to find where the server is or if the server actually exist. Remember that DHCP works using broadcast traffic in some of the steps. If Forwarding UDP broadcast traffic didn’t exist it will be needed to have one DHCP server on every VLAN. If you use DHCP, and you are, you will probably have hosts in different VLANs and all of them need to get the IP address from DHCP. Typically the broadcast domain border is router or a Layer’s 3 switch VLAN interface. Although this is normal for most of broadcast traffic there needs to be a way to forward some kinds of broadcast traffic across that border. In normal networking theory it’s normal that broadcast initiated on host inside one VLAN will get to all host inside that VLAN but it will not get across to other VLAN. If you have more that one broadcast domains in your local network, let’s say that you have three VLANs. A lower value raises average throughput by utilizing MTU capacity more efficiently.We will speak here about some basics about Forwarding UDP broadcast traffic. If you were wondering what Forwarding UDP broadcast traffic actually is I will try to explain it here in few words.
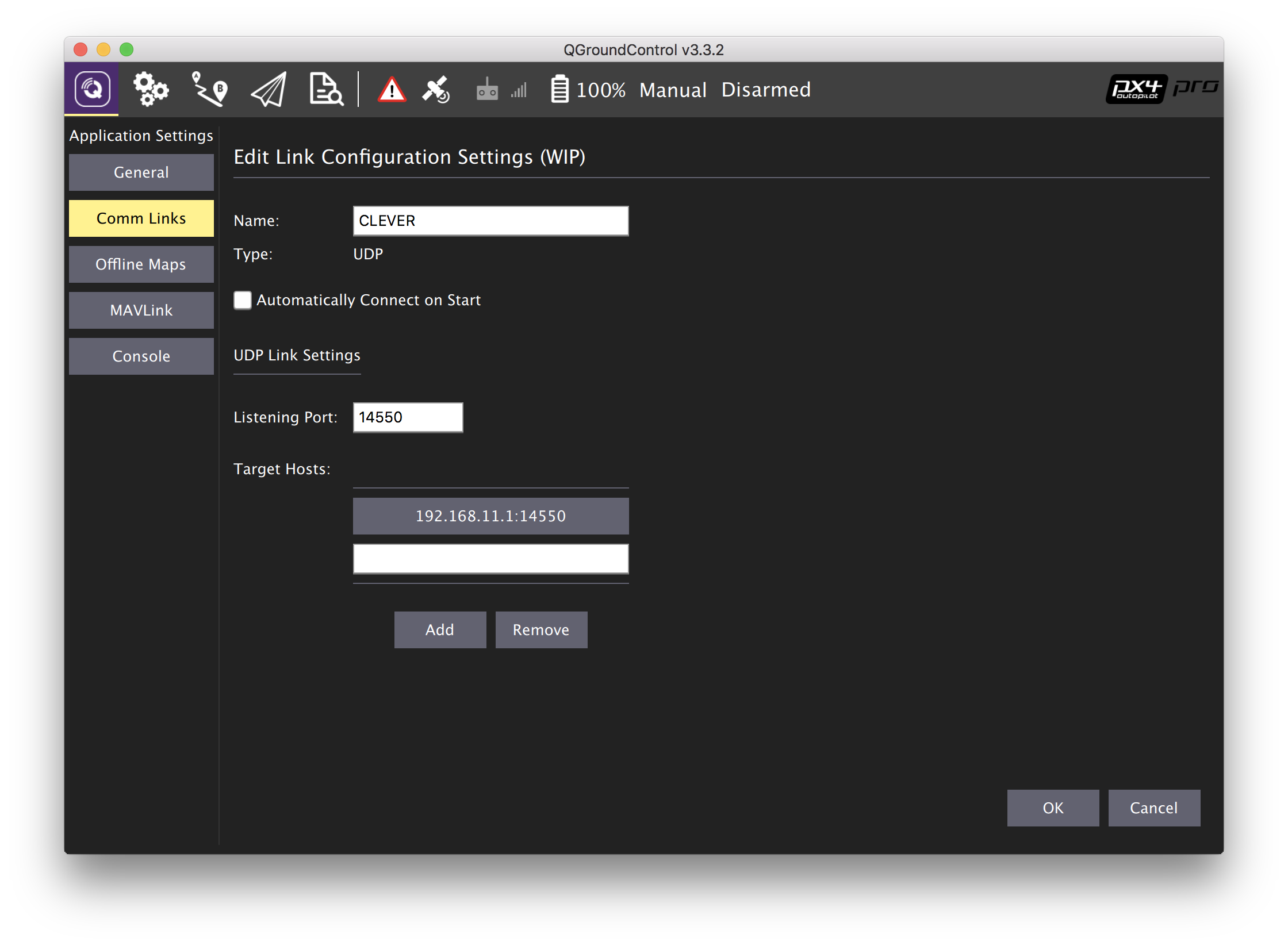
 If the number of packets overwhelms any receiver, try a lower value.
If the number of packets overwhelms any receiver, try a lower value.  To reduce average latency, try raising the value. Select an initial value based on capacity of the receiving CPUs to handle NIC interrupts. To begin, try a value within the range 50,000 to 150,000 packets per second. The general goal is to determine the highest value that does not overwhelm any receiving hardware. Use these guidelines as you empirically tune this parameter: When an application rapidly sends one small message per send call, then adjust the packet send limit to increase throughput efficiency. However, if slow receivers report dataloss, then consider tuning the packet send limit (see the next item). For best results in most situations, set the packet send limit to zero. When an application sends batches of several messages in its send calls, it is probably already using UDP bandwidth efficiently. (This sending parameter has no effect at the receiving end.) Tune the packet send limit parameter on the senders’ transports. When an inbound packet arrives, the cost of the NIC interrupt is independent of the size of the data in the packet. Hardware limits on the number of NIC I/O interrupts translate into limits on the receiver’s inbound message rate. However, even if the data send rate is low, a high packet send rate can still overwhelm a receiver. Limiting the packet send rate also limits the data send rate (bytes per second), because the data send rate varies with the packet rate and the data sizes of the packets. To prevent these scenarios, you can limit the rate at which sending programs transmit UDP packets to the network.Īdministrators can empirically tune the flow of data packets from sending programs by adjusting the packet send limit, which is a required property of UDP-based transports. With UDP-based transports such as multicast, fast sending programs can overwhelm slower receiving programs, which could result in retransmission-related latency, extra resource consumption of CPU cycles and network bandwidth, retransmission storms, or data loss.
To reduce average latency, try raising the value. Select an initial value based on capacity of the receiving CPUs to handle NIC interrupts. To begin, try a value within the range 50,000 to 150,000 packets per second. The general goal is to determine the highest value that does not overwhelm any receiving hardware. Use these guidelines as you empirically tune this parameter: When an application rapidly sends one small message per send call, then adjust the packet send limit to increase throughput efficiency. However, if slow receivers report dataloss, then consider tuning the packet send limit (see the next item). For best results in most situations, set the packet send limit to zero. When an application sends batches of several messages in its send calls, it is probably already using UDP bandwidth efficiently. (This sending parameter has no effect at the receiving end.) Tune the packet send limit parameter on the senders’ transports. When an inbound packet arrives, the cost of the NIC interrupt is independent of the size of the data in the packet. Hardware limits on the number of NIC I/O interrupts translate into limits on the receiver’s inbound message rate. However, even if the data send rate is low, a high packet send rate can still overwhelm a receiver. Limiting the packet send rate also limits the data send rate (bytes per second), because the data send rate varies with the packet rate and the data sizes of the packets. To prevent these scenarios, you can limit the rate at which sending programs transmit UDP packets to the network.Īdministrators can empirically tune the flow of data packets from sending programs by adjusting the packet send limit, which is a required property of UDP-based transports. With UDP-based transports such as multicast, fast sending programs can overwhelm slower receiving programs, which could result in retransmission-related latency, extra resource consumption of CPU cycles and network bandwidth, retransmission storms, or data loss.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
